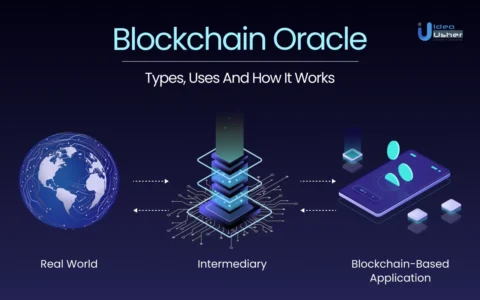
In the ever-evolving landscape of blockchain technology, one of the biggest challenges has been connecting decentralized systems with real-world data. Blockchains, by design, are closed environments — secure, immutable, and self-contained. While this makes them trustworthy for storing and validating transactions, it also creates a major limitation: they can’t directly access external information. This is where oracles step in — acting as the vital bridge between the blockchain and the outside world.
Let’s dive deep into how oracles work, why they’re so essential, and how they’re shaping the future of decentralized applications (dApps), finance, and beyond.
🔗 What Exactly Are Blockchain Oracles?
In simple terms, an oracle is a service or mechanism that supplies real-world data to a blockchain. It functions as an information conduit, feeding smart contracts with external inputs like weather reports, market prices, election results, or even IoT sensor data.
Smart contracts — the automated programs that execute based on predefined conditions — can only make decisions based on the information available within the blockchain. If a contract needs to verify a real-world event (“Did Bitcoin cross $70,000?” or “Did a shipment arrive at its destination?”), it needs a trusted source to confirm it.
That trusted source is the oracle.
For example:
- In DeFi, oracles provide real-time price feeds for assets like ETH/USD.
- In insurance, they can verify events like flight delays or rainfall data.
- In supply chains, they track product movements using IoT devices and sensors.
⚙️ How Do Oracles Work?
To understand their function, think of oracles as middleware between the blockchain and external data sources. Their primary job is to fetch, verify, and deliver data to smart contracts in a secure and tamper-proof way.
Here’s the general workflow:
- A smart contract requests data.
Example: A DeFi app wants to know the current price of ETH. - The oracle gathers data from external APIs or feeds.
It collects price information from various exchanges. - The oracle verifies and aggregates the data.
Multiple data points are compared to ensure accuracy. - The oracle sends the verified data back to the blockchain.
The smart contract receives the data and executes accordingly.
This ensures that blockchain applications can operate with real-time, accurate information while maintaining the network’s decentralization and trustworthiness.
🧠 Types of Blockchain Oracles
Oracles come in several types, depending on their data sources and functionality. Understanding these variations helps clarify how flexible and powerful they can be:
- Software Oracles:
Pull data from online sources — like market prices, APIs, and databases.
Example: Price feeds for DeFi protocols such as Chainlink or Band Protocol. - Hardware Oracles:
Collect data from the physical world using IoT devices, sensors, or RFID tags.
Example: Tracking shipments or verifying temperature conditions for perishable goods. - Inbound Oracles:
Bring real-world data into the blockchain.
Example: A sports oracle providing live match results. - Outbound Oracles:
Send blockchain data to the outside world.
Example: Triggering a payment or unlocking a smart lock after on-chain verification. - Consensus Oracles:
Aggregate data from multiple sources and reach consensus to prevent manipulation.
Example: Chainlink’s decentralized network of nodes verifying data before submission.
🧩 Why Oracles Matter: The Real-World Impact
Oracles play a foundational role in expanding blockchain’s use cases beyond simple transactions. They enable a fusion of digital and physical realities, making smart contracts smarter and more practical.
Here’s how they’re transforming industries:
- DeFi (Decentralized Finance):
Oracles power most DeFi platforms by providing real-time asset pricing, ensuring fair lending, borrowing, and trading mechanisms. Without oracles, platforms like Aave or Synthetix couldn’t function effectively. - Insurance:
Smart contracts can automatically execute claims when oracle data confirms an event (e.g., a flight cancellation). This removes the need for manual verification and speeds up processes. - Supply Chain Management:
Hardware oracles can record every step of a product’s journey, verifying authenticity and preventing fraud — a game-changer for luxury goods, food, and pharmaceuticals. - Prediction Markets:
Platforms like Augur or Polymarket rely on oracles to confirm real-world outcomes, such as election results or sports scores. - NFTs and Gaming:
Oracles can inject real-world events into games, enabling dynamic NFTs that evolve based on external conditions (like weather or stock prices).
⚠️ The Oracle Problem: Trust and Security
While oracles are essential, they also introduce a paradox known as the Oracle Problem — the challenge of trusting external data in a trustless system.
Blockchains are secure because they rely on decentralized consensus. However, if an oracle is centralized or compromised, it becomes a single point of failure, undermining the entire smart contract.
Imagine a DeFi protocol that relies on one oracle for ETH prices — if that oracle is hacked or provides wrong data, millions could be lost instantly.
To solve this, modern oracle networks like Chainlink, API3, and Band Protocol use decentralized oracle systems, where multiple nodes fetch and verify data before submitting it to the blockchain. This reduces manipulation risk and increases reliability.
🌍 The Future of Oracles in Web3
As blockchain technology evolves, oracles are becoming more advanced, adaptive, and autonomous. With developments like AI integration, cross-chain oracles, and trusted hardware (like Intel SGX), the future of decentralized data is bright.
Upcoming trends include:
- Cross-chain interoperability: Oracles connecting multiple blockchains seamlessly.
- AI-driven validation: Smarter oracles that assess data credibility using machine learning.
- Zero-knowledge proofs: Ensuring data integrity without revealing sensitive information.
- Real-time global connectivity: Oracles powering the Internet of Things (IoT) with blockchain-backed trust.
🧭 Final Thoughts
Oracles are the unsung heroes of the blockchain revolution — the silent connectors that enable smart contracts to interact with reality. Without them, most blockchain applications would be confined to their digital bubbles, unable to reflect the dynamic world we live in.
As blockchain technology scales, oracles will become the backbone of reliability, accuracy, and automation in the decentralized ecosystem. They are not just messengers of data — they are bridges of trust, bringing the power of blockchain closer to the real world.